Learnings and next steps
One of the main components of the HACK Project is gathering learnings and sharing best practices for policy and investments advocacy. There were several important learnings derived from the project implementation, that include:
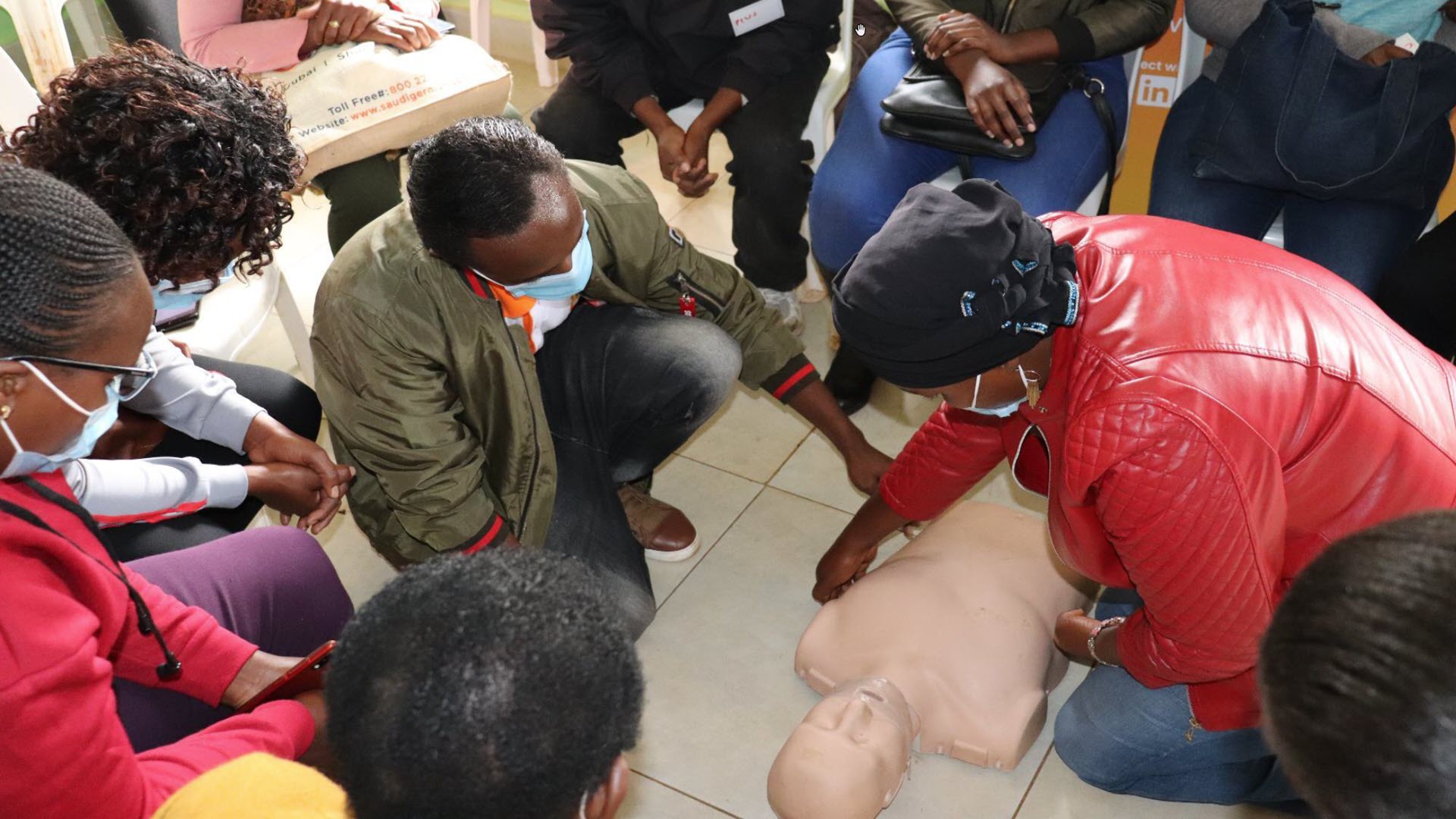
- Importance of capacity building: essential skills such as ECG examination and interpretation were initially lacking among the different levels of healthcare workers working in the target facilities. STEMI services preparedness depends on healthcare workers having the capacity to recognize symptoms, diagnose and manage the disease. For sustained impact and continuity there should be focus on continuous capacity building.
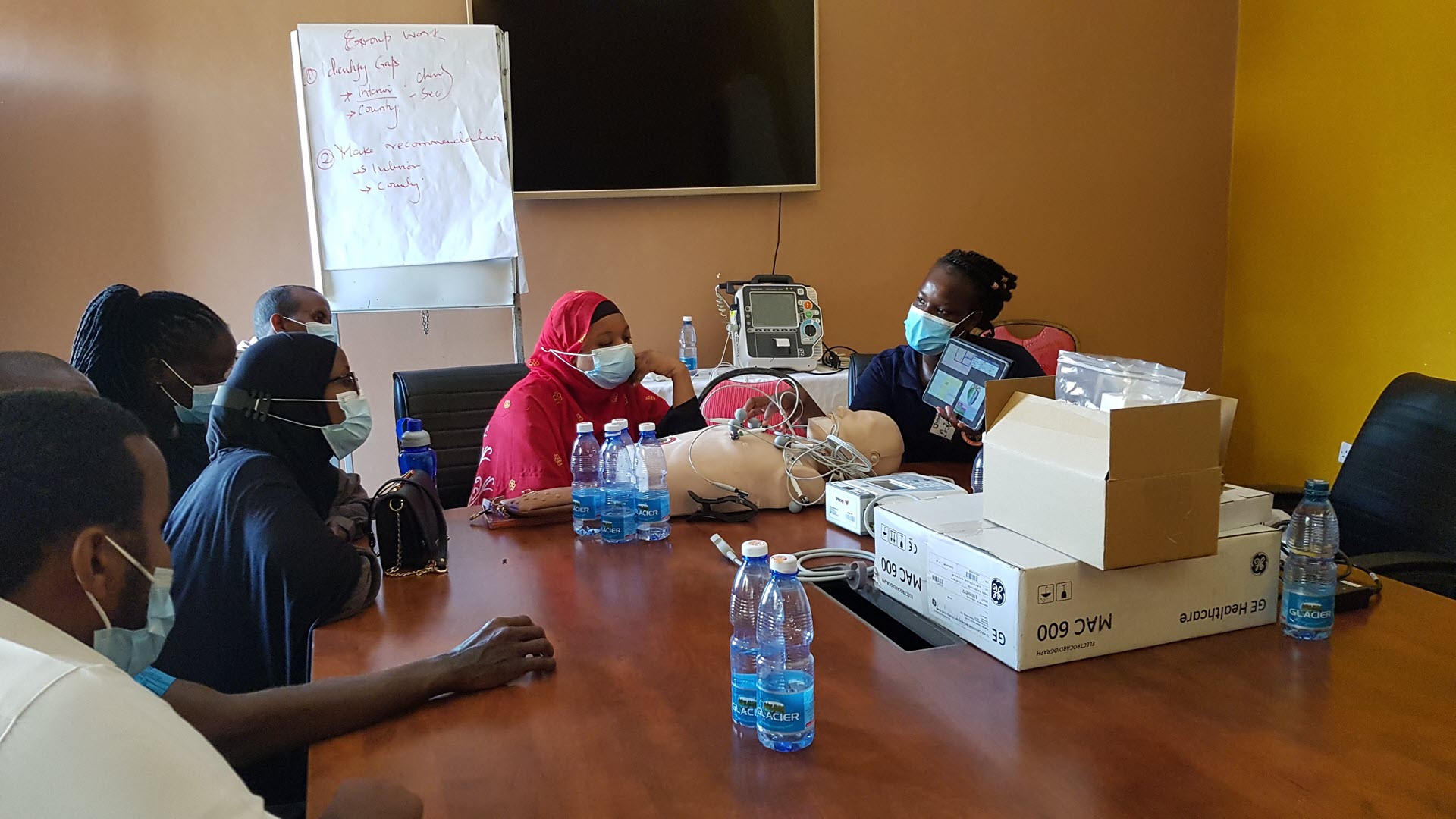
- Importance of governance: good governance can help promote effective health service delivery, especially when informed by data and evidence. The project supported the development of STEMI protocols which were initially non-existent in the target facilities. Guidelines and protocols are necessary to guide health care workers on diagnosis, optimal treatment options and form the basis for quality improvement audits and improvements at the hospital level.
- Equipping health facilities and proper implementation of policies: while the cardiovascular guidelines in Kenya outline the suite of cardiovascular disease services that should be available at each level of care, there are gaps both in the services offered and in the equipment available to offer these services. Gaps in the operationalization and implementation of policies will often result in decreased efficiency of health systems.
- Stakeholder management: The insights from the implementation process highlight the need to involve key decision makers, as well as the importance of government support and political good will to ensure successful implementation and sustainability.
The project provides important lessons on the level of preparedness for heart attack care in Kenya, the type of investments needed, and provides tools for scaling such models. The pilot in the three counties can therefore be seen as a prototype that hopefully will later be implemented to more counties in Kenya and beyond.